#2 USB-RS232C I/FでWS2812Bを駆動 基礎編
前記事C++ Builder CE 周辺拡張の続編です。今回は、USBにつないだRS232CへのI/F経由でWS2812Bの8素子LEDを駆動してみます。使用するI/FはFT234X 超小型USBシリアル変換モジュールです。秋月電子で購入しました。
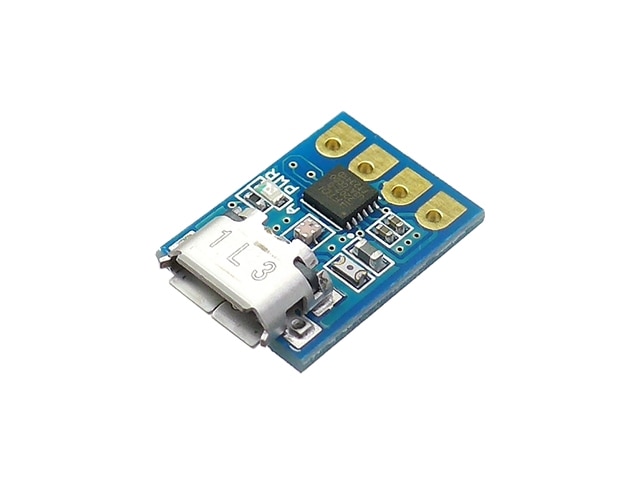

こんな外観ですけど、このままではとりまわしが困難なので、同梱の4ピンのヘッダーは半田付けします。ドライブする方のLEDは、基礎編では、
こんな外観の8個直列のものを使ってみます。amazonで”ws2812b”とでも検索するとありとあらゆる素子数と形状のものを扱っています。テープとして供給されていて、好きなところでカットして任意の素子数で使うことも可能です。基板の裏側は、

このようになっていますので、普通はL字側のピンヘッダーをはんだ付けして、そのヘッダーをブレッドボードに挿して配線します。結構脆いので、物理的に強い力がかからないようにする必要があります。筆者は2個セットを買いましたが、早々に一個おしゃかにしました。ご注意ください。
シリアル変換モジュールをPCにつなぐと、すぐに認識されます。(音がするのと、基板上の小さい青色のLEDが点灯します。)ここでCOMポートの番号を設定しておきましょう。それはWindowsのデバイスドライバーのプロパティーから設定します。
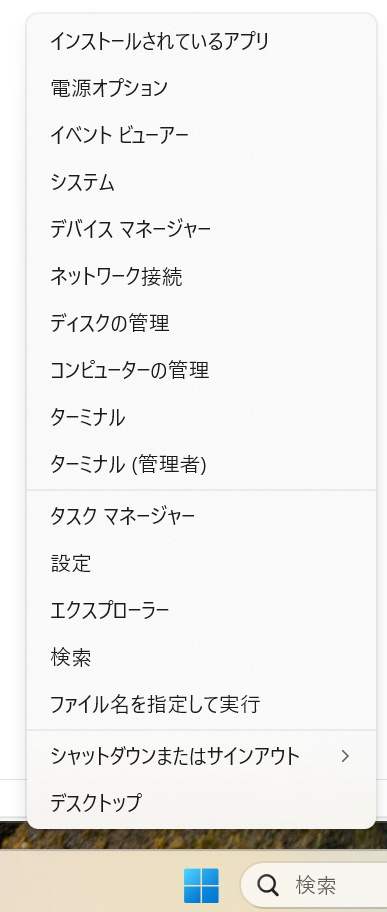
最下部の中央のWindowマークを右クリックして出てくる上記メニューで、デバイスマネージャーを選択します。
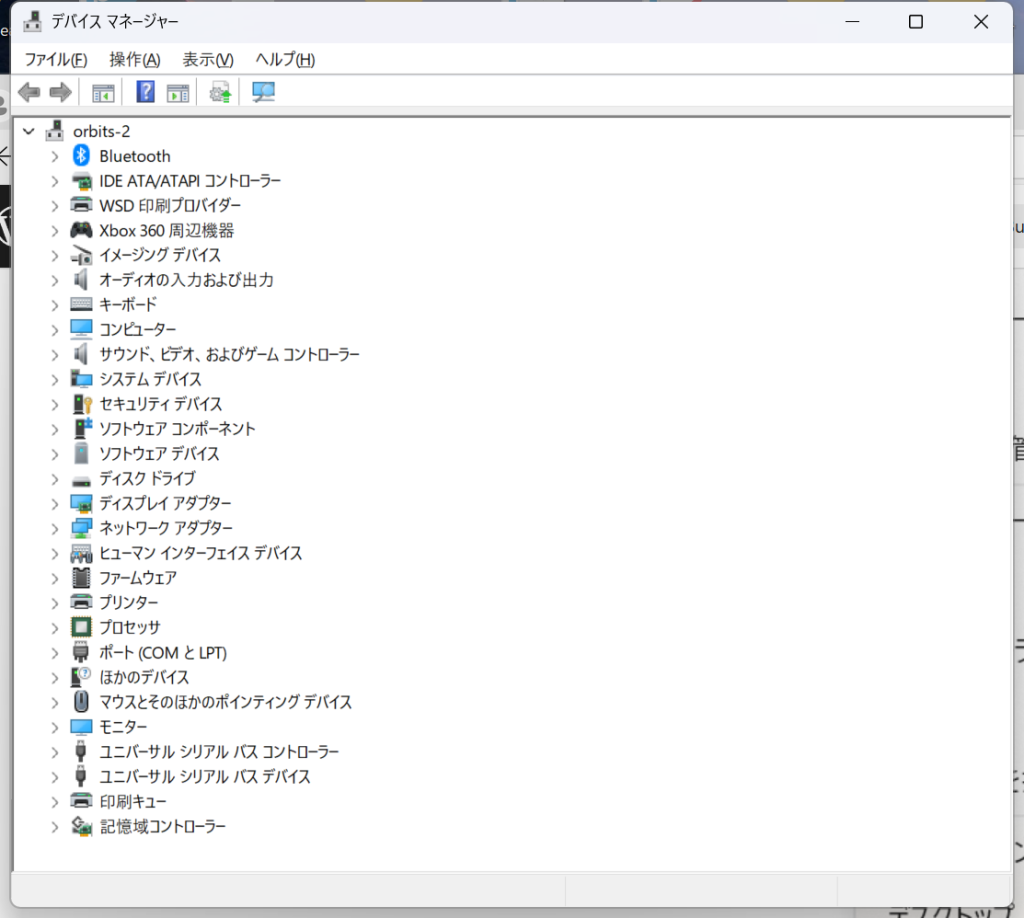
下の方にポート(COMとLPT)というのがあるので、これを選択します。
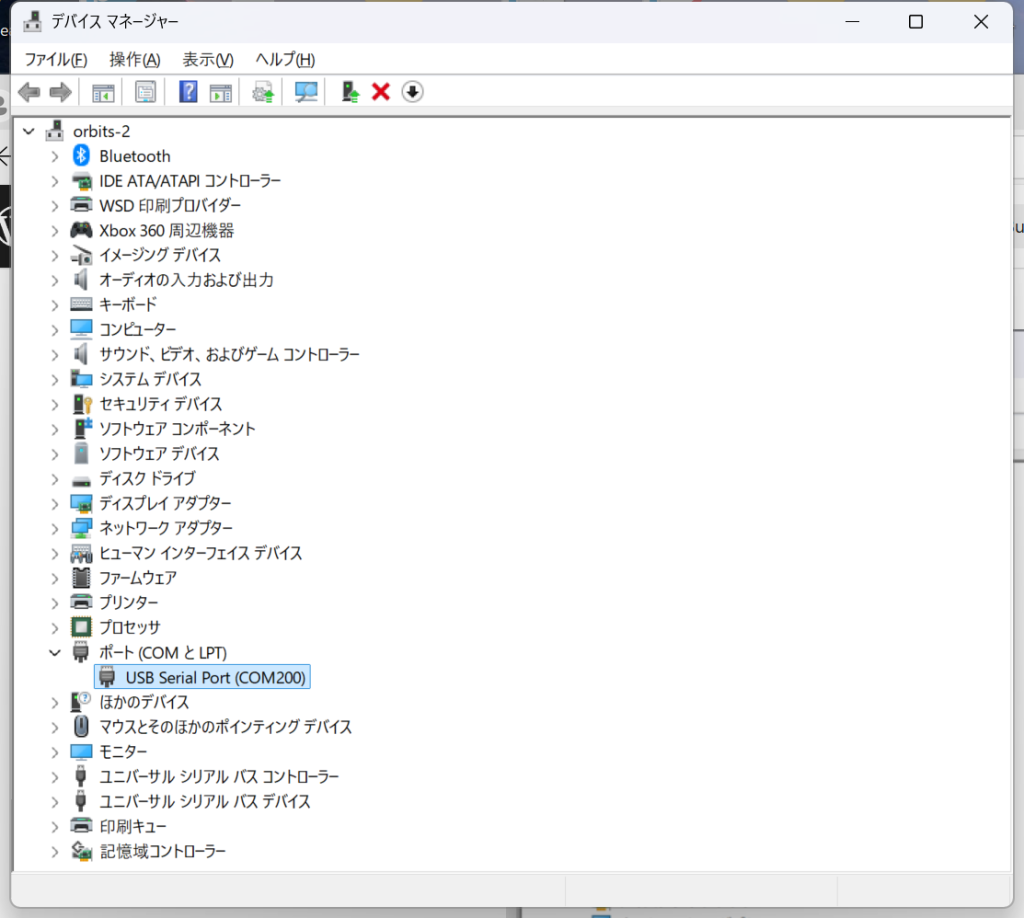
USB Serial Port(COM200)が現れるので、これを右クリックしてプロパティーを選択。最初から200にはなっていないはずです。
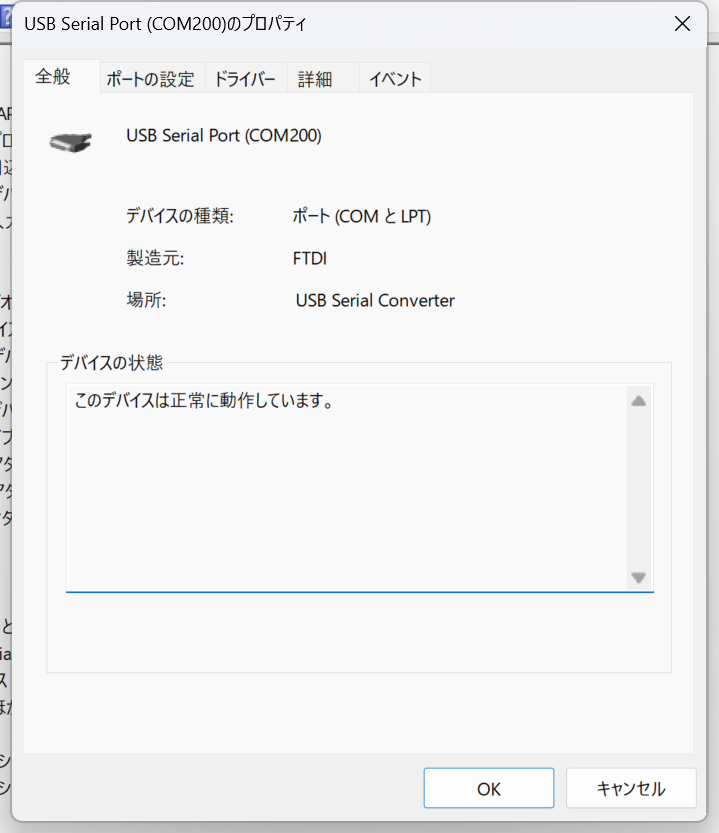
ここでポートの設定を選択。
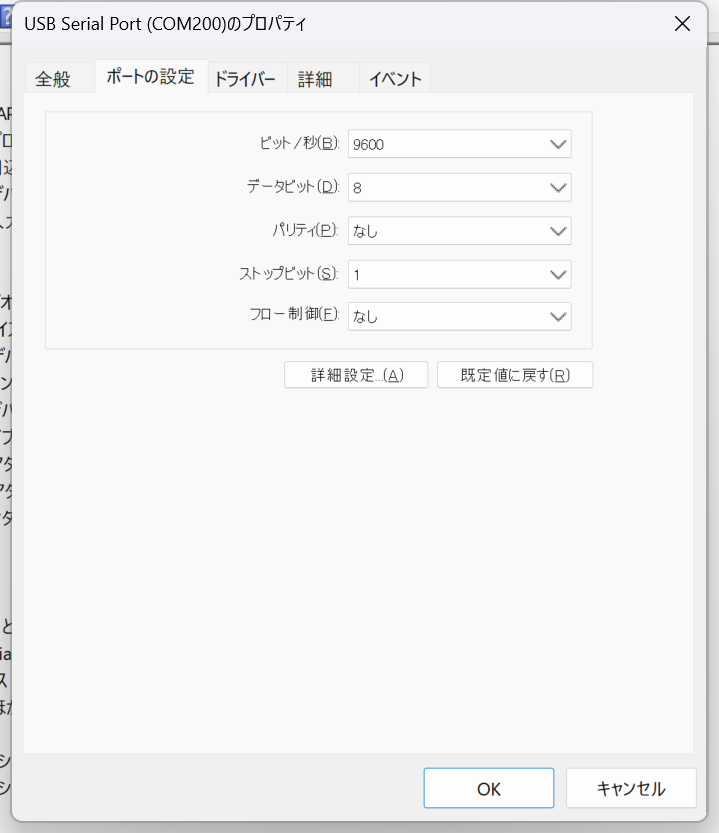
なかほどの”詳細設定”をクリック。
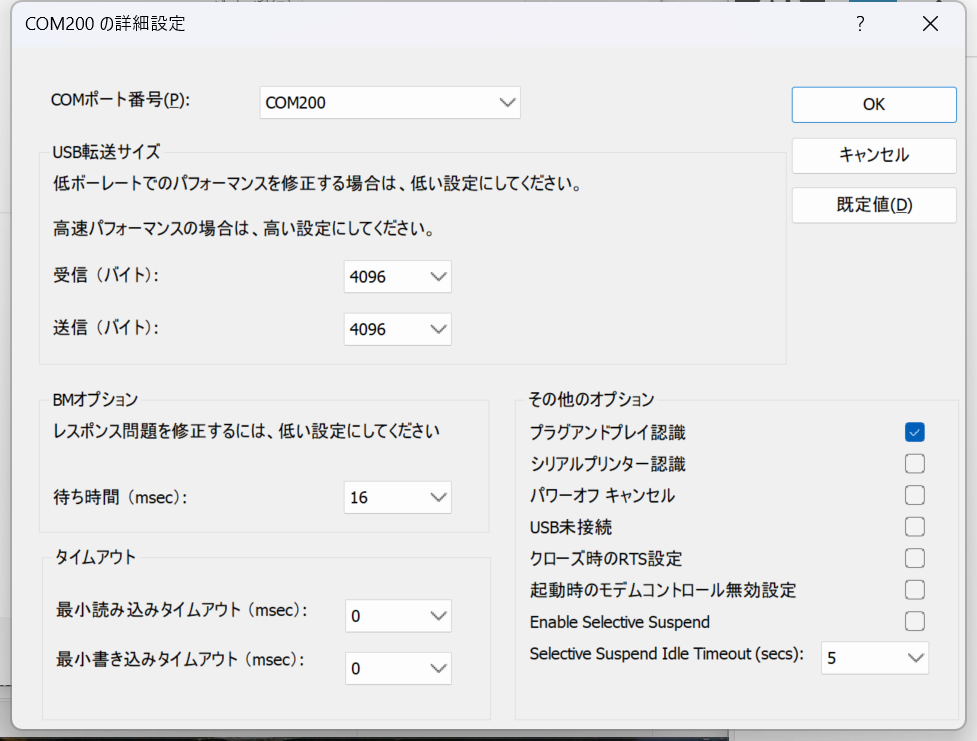
ここでCOMポート番号をCOM200に設定。今回は200に設定されいるのが前提です。で、OK。
ポート番号だけが重要で、ほかのパラメーターはプログラムから設定するのでDon’t careです。
最下層のドライバとしてRS232Cを設定したり、読んだり、書いたりするルーチンが必要ですが、一応C++な世界なのでクラスになっているものを拝借して使っています。これまた出自が不明です。ご存じの方いらっしゃったらコメントを。Githubのどこかだったと思いますが、消滅してて検索にかからないのかもしれません。まずはヘッダーSerialPort.hから、
#ifndef SerialPort_H
#define SerialPort_H
#include <cstdlib>
#include <iostream>
#include <stdio.h>
#include <stdlib.h>
#include <map>
#include <string>
#include <string.h>
#include <windows.h>
#include <conio.h>
#define RX_SIZE 4096 // in buffer size
#define TX_SIZE 4096 // out buffer size
#define MAX_WAIT_READ 5000 // max waiting time (in ms)
class SerialPort
{
public :
SerialPort();
virtual ~SerialPort();
bool Open(std::string s);
bool Read(char* buffer, unsigned int nBytesToRead, unsigned int *pBytesRead);
bool Write(unsigned char *buffer, unsigned int nBytesToWrite, unsigned int *pBytesWritten);
bool Close();
private :
HANDLE g_hCOM;
COMMTIMEOUTS g_cto;
DCB g_dcb;
void Init();
};
#endifつぎはSerialPort.cppです。
#include "SerialPort.h"
using namespace std;
SerialPort::SerialPort()
{
this->Init();
}
SerialPort::~SerialPort()
{
this->Close();
}
void SerialPort::Init()
{
g_hCOM = NULL;
COMMTIMEOUTS t_g_cto =
{
//MAX_WAIT_READ, /* ReadIntervalTimeOut */
0, /* ReadTotalTimeOutMultiplier */
//MAX_WAIT_READ, /* ReadTotalTimeOutConstant */
0, /* WriteTotalTimeOutMultiplier */
0 /* WriteTotalTimeOutConstant */
};
memcpy(&g_cto, &t_g_cto, sizeof(t_g_cto));
// port configuration
DCB t_g_dcb =
{
sizeof(DCB), /* DCBlength */
3000000, //19200, /* BaudRate */
TRUE, /* fBinary */
FALSE, /* fParity */
FALSE, /* fOutxCtsFlow */
FALSE, /* fOutxDsrFlow */
DTR_CONTROL_ENABLE, /* fDtrControl */
FALSE, /* fDsrSensitivity */
FALSE, /* fTXContinueOnXoff */
FALSE, /* fOutX */
FALSE, /* fInX */
FALSE, /* fErrorChar */
FALSE, /* fNull */
RTS_CONTROL_ENABLE, /* fRtsControl */
FALSE, /* fAbortOnError */
0, /* fDummy2 */
0, /* wReserved */
0x100, /* XonLim */
0x100, /* XoffLim */
8, /* ByteSize */
NOPARITY, /* Parity */
ONESTOPBIT, /* StopBits */
0x11, /* XonChar */
0x13, /* XoffChar */
'?', /* ErrorChar */
0x1A, /* EofChar */
0x10 /* EvtChar */
};
memcpy(&g_dcb, &t_g_dcb, sizeof(t_g_dcb));
}
bool SerialPort::Open(std::string nId)
{
nId = "\\\\.\\COM" + nId;
std::wstring FilePath(nId.begin(), nId.end());
g_hCOM = CreateFile(FilePath.c_str(), GENERIC_READ|GENERIC_WRITE, 0, NULL, OPEN_EXISTING, FILE_ATTRIBUTE_SYSTEM, NULL);
if (g_hCOM == INVALID_HANDLE_VALUE)
return false;
SetupComm(g_hCOM, RX_SIZE, TX_SIZE);
if (!SetCommTimeouts(g_hCOM, &g_cto) || !SetCommState(g_hCOM, &g_dcb))
{
CloseHandle(g_hCOM);
return false;
}
PurgeComm(g_hCOM, PURGE_TXCLEAR|PURGE_RXCLEAR|PURGE_TXABORT|PURGE_RXABORT);
EscapeCommFunction(g_hCOM, SETDTR);
return true;
}
bool SerialPort::Close()
{
return CloseHandle(g_hCOM);
}
bool SerialPort::Read(char *buffer, unsigned int nBytesToRead, unsigned int *readBytes)
{
int tmp(0);
*readBytes = 0;
while (*readBytes < nBytesToRead)
{
if (!ReadFile(g_hCOM, buffer + *readBytes, nBytesToRead - *readBytes, (DWORD*)&tmp, NULL))
return false;
*readBytes += tmp;
}
return true;
}
bool SerialPort::Write(unsigned char *buffer, unsigned int nBytesToWrite, unsigned int *pBytesWritten)
{
int tmp(0);
*pBytesWritten = 0;
while (*pBytesWritten < nBytesToWrite)
{
if (!WriteFile(g_hCOM, buffer + *pBytesWritten, nBytesToWrite - *pBytesWritten, (DWORD*)&tmp, NULL))
return false;
*pBytesWritten += tmp;
}
return true;
}ここで設定しているボーレート他がエッセンシャルです。タイミング的に動いてます。レベルの方の話で言うと、本来は純粋なRS232Cはロジックレベル(0-5V)とは違うのですが、動いてますので深く追求しません。タイミングやレベルの検討をされている方はいらっしゃるようです。後で出てくる動画で明らかなように一応所望の動作はしているようです。
これでドライブするWS2812BなLED列も一応クラスで表現します。これ以降は完全に自作です。まず、ws2812b.hですが、
#ifndef __ws2812b
#define __ws2812b
#include <stdint.h>
#include "SerialPort.h"
struct CCRGB {
union {
struct {
union {
uint8_t r;
uint8_t red;
};
union {
uint8_t g;
uint8_t green;
};
union {
uint8_t b;
uint8_t blue;
};
};
uint8_t raw[3];
};
inline CCRGB& setRGB(uint8_t nr, uint8_t ng, uint8_t nb)//__attribute__((always_inline))
{
r = nr;
g = ng;
b = nb;
return *this;
}
};
class ws2812b {
public:
ws2812b( int numofleds, CCRGB* leds );
void showleds();
void clear();
private:
const unsigned char table[4] = { 0xef, 0xcf, 0xee, 0xce };
int lednum;
CCRGB* array;
SerialPort port;
unsigned bufsize;
unsigned char* obuf;
};
#endifつぎが、ws2812b.cppです。
#include <stdio.h>
#include "SerialPort.h"
#include "ws2812b.h"
ws2812b::ws2812b( int numleds, CCRGB* leds)
{
//SerialPort wrap;
//black.setRGB(0, 0, 0) :
if( !port.Open("200"))
{
fprintf(stderr, "can't open port\n");
return;
}
lednum = numleds;
array = leds;
bufsize = 8 / 2 * 3 * numleds;
obuf = (unsigned char*)malloc(bufsize); // total bytes required
if( !obuf ){
fprintf(stderr, "can't alloc output buffer\n");
return;
}
}
void ws2812b::showleds()
{
unsigned int tr;
int index = 0;
for( int i = 0 ; i < lednum ; i++ ){
obuf[index++] = table[array[i].g >> 6 & 0x03];
obuf[index++] = table[array[i].g >> 4 & 0x03];
obuf[index++] = table[array[i].g >> 2 & 0x03];
obuf[index++] = table[array[i].g >> 0 & 0x03];
obuf[index++] = table[array[i].r >> 6 & 0x03];
obuf[index++] = table[array[i].r >> 4 & 0x03];
obuf[index++] = table[array[i].r >> 2 & 0x03];
obuf[index++] = table[array[i].r >> 0 & 0x03];
obuf[index++] = table[array[i].b >> 6 & 0x03];
obuf[index++] = table[array[i].b >> 4 & 0x03];
obuf[index++] = table[array[i].b >> 2 & 0x03];
obuf[index++] = table[array[i].b >> 0 & 0x03];
}
port.Write(obuf, bufsize, &tr);
}
void ws2812b::clear()
{
for (int i = 0; i < lednum; i++)
array[i].setRGB(0, 0, 0);
showleds();
}今見たらmallocとかCの匂いがしますね。(笑)ま、動いているのでよしとしてください。
フォームのデザインですが、
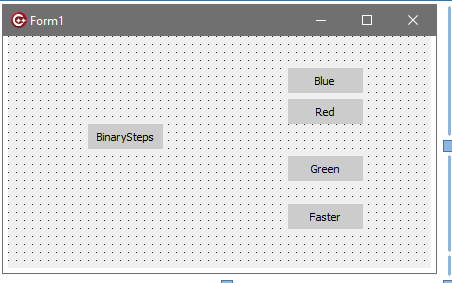
のように適宜ボタンを置き、適宜Captionを付けて、Unit.1は省略して、Unit1.cppは、
#include <vcl.h>
#pragma hdrstop
#include "ws2812b.h"
#include "Unit1.h"
//---------------------------------------------------------------------------
#pragma package(smart_init)
#pragma resource "*.dfm"
#define NUMLEDS 8
TForm1 *Form1;
CCRGB leds[NUMLEDS];
ws2812b* aled;//= new ws2812b(NUMLEDS, leds);
//---------------------------------------------------------------------------
__fastcall TForm1::TForm1(TComponent* Owner)
: TForm(Owner)
{
aled = new ws2812b(NUMLEDS, leds);
aled->clear();
}
//---------------------------------------------------------------------------
void __fastcall TForm1::Button1Click(TObject *Sender)
{
// B
//aled->clear();
for (int i = 1; i < NUMLEDS+1 ; i++) {
leds[i - 1].setRGB(0, 0, 30);
aled->showleds();
Sleep(700);
leds[i-1].setRGB(0,0,0);
}
//getchar();
aled->clear();
}
//---------------------------------------------------------------------------
void __fastcall TForm1::Button2Click(TObject *Sender)
{
// R
int k;
//aled->clear();
for (k = 0; k < NUMLEDS ; k++) {
leds[k].setRGB(30, 0, 0);
aled->showleds();
Sleep(700);
leds[k].setRGB(0,0,0);
}
aled->clear();
}
//---------------------------------------------------------------------------
void __fastcall TForm1::Button3Click(TObject *Sender)
{
// G
//aled->clear();
for (int i = 0; i < NUMLEDS ; i++) {
leds[i].setRGB(0, 30, 0);
aled->showleds();
Sleep(700);
leds[i].setRGB(0,0,0);
}
aled->clear();
}
//---------------------------------------------------------------------------
void __fastcall TForm1::Button4Click(TObject *Sender)
{
//aled->clear();
for( int i = 0 ; i < NUMLEDS ; i++ ){
leds[i].setRGB(30,0,0);
aled->showleds();
Sleep(350);
leds[i].setRGB(0,0,0);
//aled->clear();
}
aled->clear();
}
//---------------------------------------------------------------------------
void __fastcall TForm1::BinaryStepsClick(TObject *Sender)
{
//aled->clear();
int seed = 1;
for (int i = 0; i < NUMLEDS ; i++) {
leds[i].setRGB(seed, seed, seed);
aled->showleds();
Sleep(700);
seed *= 2;
// 1,2,4,8,16,32,64,128
//leds[i].setRGB(0,0,0);
}
Sleep(500);
aled->clear();
}
//---------------------------------------------------------------------------
となってます。一例に過ぎません。使い方ですが、
#define NUMLEDS 8
CCRGB leds[NUMLEDS];
ws2812b* aled = new ws2812b(NUMLEDS, leds);と宣言すれば使えます。leds[0]~leds[NUMLEDS-1]までデータ(RGB値)をセットしてから、led[i].setRGB(rvalue,bvalue,gvalue);でRGB値をi番目のLEDにセットできます。全体は、
aled->showleds();で表示されます。aled->clear();ですべてオフとなります。Unit1.h,Unit1.cppにSerialPort.hとSerialPort.cppさらにws2812b.hとws2812b.cppを加えてBuild and Runすると、
この二つは700msの点灯時間ですが、時間を半分にすると。
次は、RGB値を1,2,4,8,16,32,64,128と変化させた場合です。
結構128では眩しいし、動画のダイナミックレンジを超えているような気がします。MAXの明るさは、このさらに倍になります。電源負荷が心配なのでやりませんけど。ま、短時間なら大丈夫かもしれませんが、自己責任でトライしてください。眩しくて観ていられないかもしれません。
動画撮影は、Nikon D7500を拙作のCamera Remote Control64で駆動https://www.vector.co.jp/soft/winnt/hardware/se526600.htmlして行いました。レリーズ使わないので、手ぶれしないし、PC側に動画ファイルが得られて便利です。このシリーズの次はもう少し手の込んだ例を示します。



コメント
[…] ガラクタの山に埋もれていた懐かしいUSB I/Fでの出力電圧および出力電流をモニターするアダプタが発掘されたので、前記事C++ Builder CE 周辺拡張で問題視した負荷電流値を一応確認しておこうという記事です。まずアダプタ自体は、 […]